ISO 9001 / ISO 27001
- gözde alnıaçık
- Aug 9, 2024
- 20 min read
4. CONTEXT OF THE ORGANIZATION
Determining the factors that affect your company will guide you in establishing your system.
4.1 Understanding the Organization's Context
The factors that the management system affects and is affected by should be determined as a context.
The issues that are affected can be defined as external context, and the issues that it affects can be defined as internal context.
Note: Internal and external issues are randomly sampled with a general approach, you need to customize and elaborate specific to your company's scope.
4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties
4.3 Scope
Your company's management system determines its boundaries
Subjects of activity
Activity venues
Security and technological infrastructure should be described
In addition, if there is an item that you have excluded from the above elements or the standard, you must describe it here with the reasons.
Example: XYZ Company scope
Subjects of activity: website and mobile application design services
The activity areas are the head office located in Istanbul, Tuzla …., the branch office in Ankara Gölbaşı and the website XYZ design @....
4.4 Management System and Processes
The administrative, support and operational processes that your company needs should be determined and the procedures should be described in accordance with the determined method in accordance with ISO 900 1 and 27001. These processes may be aimed at measuring/developing customer satisfaction, evaluating process performance, organizing training, implementing internal audits, organizing corrective actions, defining access permissions and access authorizations. In addition to these examples, operational processes should also be prepared for the necessary planning, application control, etc. stages in accordance with the company's own operation.
You can describe your process under a procedure, draw a flow chart, or determine an alternative method.
Processes should be continually reviewed and updated when necessary, based on continuous improvement principles.
Below, an example of a process interaction diagram prepared for a company engaged in Engineering Management and R&D activities is given, and immediately afterwards, an example of an "Internal Audit Process" prepared with the process flow diagram logic according to the process requirements of the internal audit process in the diagram is shared.
Note: The examples shared in the figures above are based entirely on assumptions. They can be changed or improved depending on the scope, field of activity and company structure of the companies.
5. LEADERSHIP
5.1 Leadership and Commitment
By the top management;
Quality and Information Security Policy should be created with a strategic plan.
Necessary processes that comply with system conditions must be determined and secured.
Encouraging the use of a process approach and risk-based thinking,
The existence and accessibility of the resources required for the system must be ensured.
Creating staff awareness for the effective operation of the system
Continuous improvement should be encouraged
5.2 Policy
By the Top Management,
In line with the purpose of the organization,
Containing quality and information security objectives or providing a framework for determining quality and information security objectives,
Contains a commitment to meet applicable requirements regarding quality and information security and a commitment to continuous improvement of the management system.
A Quality and Information Security Policy should be established.
Quality and Information Security Policy;
Must be available as written information,
It should be announced within the organization and (can be posted on the notice board, sent to employees via e-mail, etc.)
Must be accessible to appropriate interested parties. (Can be shared on the website)
5.3 Duties, Powers and Responsibilities
Top management should assign responsibility and authority for:
a) To ensure that the quality and information security management system complies with the requirements of this standard.
b) Reporting to senior management on the performance of the quality and information security management system.
6. PLANNING
6.1 Risk and Opportunity Identification Activities
6.1.1 General
In your company
a) Ensuring that the intended outputs of the quality and information security management system can be achieved,
b) Preventing or reducing undesirable effects,
c) Achieving continuous improvement,
Risks and opportunities should be determined for,
Activities to address risks and opportunities should be identified and their effectiveness evaluated.
All controls required for the implementation of the selected information security risk processing options should be determined.
When determining control methods, the control criteria given in ANNEX-A must be taken into account.
If necessary, new risk processing methods can be determined or outsourced.
Risk assessment and acceptance criteria should be determined.
Risk owners should be identified
Risk levels should be determined by evaluating possible problems resulting from the realization of risks.
Risk assessment should be carried out
6.1.2 Risk assessment
Risks related to loss of confidentiality, integrity and accessibility of information within the scope of the management system should be identified.
The organization must maintain written information regarding the information security risk assessment process.
6.2 Goals and Planning to Achieve Them
Your company should set goals that meet the following criteria:
Must be consistent with policy,
Must be measurable (if applicable),
Take into account applicable information security requirements and the results of risk assessment and risk processing,
The set goals should be communicated to employees and updated accordingly.
Written information regarding information security objectives should be maintained.

While determining the targets,
What to do,
What resources will be required,
Who will be responsible?
When will it be completed and
How to evaluate the results
It should be clearly defined

6.3 Planning Changes
In case of a change that will affect the management system
a) Purposes and potential consequences of the changes
b) Impact of the integrity of the management system
c) Availability of resources required for change
d) Authorities and responsibilities regarding the change
He/she should analyze it, make this analysis and decide on the change as a result of this analysis.
Before any change decision is made that will affect the management system,
-What will be done, when, how, by whom and with what resources must be determined.
- Are the existing resources sufficient for the change? If so, what new resource needs should be determined.
- It should be investigated what effect the result of the change will have on the company.
And after the requested analyses are completed, the change report prepared must be approved by an authorized personnel and the change must be implemented.
7. SUPPORT
7.1 Resources
7.1.1 General
It should determine and provide the resources necessary for the establishment, implementation, maintenance and continuous improvement of the management system.

Note: The examples shared above are based entirely on assumptions. They can be changed or improved depending on the scope, field of activity and company structure of the companies.
7.1.2 Persons
Your company must determine how to select new human resources and how to adapt existing human resources to the company's management systems.
For this purpose, the human resources process can be prepared and the method for selecting personnel that is suitable for the management system and in line with the company's expectations can be described.
After selecting personnel that meet the company's expectations, the necessary administrative and technical orientations should be provided to the newly hired personnel so that they can learn and adapt to the company's management systems and their own work process.
In addition, in order to ensure the awareness of the existing human resources about the company's management system and to ensure continuity in system adaptation by being informed about any changes in the standard or management system, all personnel should be given regular training explaining the relevant standards and the company's management system.
Note: Records of orientation training given to new staff and regular awareness training given to all staff should be kept as documented information.
7.1.3 Infrastructure
A list of all infrastructure resources, such as buildings, facilities, machinery, equipment, software, hardware, transportation resources, information and communication technology, etc., should be made and a tracking method should be determined for each.
In addition, the control interval should be determined according to the needs of each infrastructure resource and the control results should be processed when the time comes.
7.1.4 Environment for operation of processes
By describing the social, psychological and social environment required for the processes from within all processes, the existence or suitability of the desired environment can be interpreted during the process control phase.
7.1.5 Monitoring and measurement resources
7.1.5.1 General
By creating a monitoring measurement tracking list, you can keep track of what is subject to monitoring measurement in your company.
For example: Your list: Customer satisfaction
Process performance efficiency
Internal audit results
Degree of achievement of goals
Amount of energy use (electricity, water, natural gas, oil)
Assuming that it consists of contents, a separate monitoring measurement criterion should be determined for each item here, and the control results should be processed and evaluated by checking at intervals determined by the system.
7.1.5.2 Measurement Traceability
The validity of the measurement must be proven by calibrating the equipment used for measurement at regular intervals in accordance with international standards.
For this purpose, a calibration tracking list can be prepared, the devices subject to calibration and the calibration criteria can be entered into the list, and calibration tracking can be done through this list.
7.1.6 Corporate Information
7.2 Competence / Qualification
The qualifications of the personnel that affect the management system performance in your company should be determined, and it should be ensured that the qualifications of these personnel are secured through training or experience, and when necessary, the necessary training, documents and programs should be provided to the personnel to gain new qualifications.
Written information must be retained as evidence of personnel qualifications.
7.3 Awareness
Awareness of all personnel working within your company who affect the management system should be ensured.

7.4 Communication
It is necessary to provide clear answers to the following items by determining the internal and external communication methods in your company. This includes sharing information among staff, communication with customers, suppliers and other interested parties.
The company's communication methods and means of communication should be determined and announced to the relevant personnel.
The availability of communication resources such as telephone numbers and e-mail addresses must be ensured.
7.5 Documented Information
Information that needs to be recorded in writing due to ISO 9001 and 27001 requirements or your company's own management system needs should be determined.
The size and content of written information may vary depending on factors such as the size of the company, its field of activity, product and service type, process structure and personnel competence.
NOTE: When determining the documentation system of each company, a system specific to that company should be established by taking into consideration its relevant parties, fields of activity, product and service area, process structure, and personnel potential.
A system that works perfectly in one company may be too detailed, complex or inadequate for another company.
Written information required by the Management System;
• Quality and Information Security Scope (4.3)
•Quality and information security policy (5.2)
• Information security risk assessment process (6.1.2)
• Information security risk processing process (6.1.3)
• Information security objectives (6.2)
• Competence (7.2)
• List of external documents (7.5.3)
• Operational planning and control (8.1)
• Information security risk assessment results (8.2)
• Information security risk processing results (8.3)
• Monitoring and measurement results (9.1)
• Internal audit programs and audit results (9.2)
• Management review results (9.3)
•The nature of the nonconformities and the results of the corrective actions and follow-up actions (10.1)
Create and Update
The following should be taken into consideration when creating and updating documents in your company:
Identifying and describing (for example, a title, date, author or reference number),
b) Format (e.g., language, software version, graphics) and medium (e.g., paper, electronic), and
c) Review and approval of suitability and accuracy.
Control of Written Information
Information,
a) It must be accessible and suitable for use wherever and whenever required.
b) Protected against risks such as loss of confidentiality, improper use or loss of integrity.
To control written information, your company should consider the following activities, as appropriate:
c) Distribution, access, retrieval and use,
d) Storage and protection, including preservation of legibility,
e) Control of changes (e.g. version control) and
f) Preservation and destruction.

8. OPERATION
8.1 Operational Planning and Control
To meet the information security requirements in your company, to carry out the activities determined for risks and opportunities, and to achieve its goals;

Must plan, implement and control the necessary processes.
He/she must control planned changes and review the consequences of unintended changes and, if necessary, take action to reduce adverse effects.
Ensure that outsourced processes are identified and controlled.
Written information should be recorded to prove that processes are carried out as planned in your company.
8.2.A Information Security Risk Assessment
Taking into account the risk assessment and risk acceptance criteria determined by your company
• At planned intervals
• When significant changes are proposed or occur
Must perform risk assessment

Your company must maintain written information about the results of the information security risk assessment.
8.2B Terms for Products and Services
This article deals with the requirements that organizations determine for the products they produce or the services they provide. The requirements of the product or service and customer expectations form the basis of the determined requirements. During the planning process, the necessary features, characteristics, performance criteria and other requirements of the product or service are determined. These are important elements that determine the quality level of the product or service. In addition, the determined requirements provide guidance in the design and production stages of the product or service. In this context, customer requirements, legal regulations, standards and the organization's own policies and procedures are taken into account when determining the requirements of the product or service.
8.3.A Information Security Risk Processing
Your company must implement an information security risk handling plan.

Your company must maintain written information on the results of information security risk processing.
8.3 Product and Design Development
Planning for the design must be done before the design is realised.
For this purpose, a planning process was prepared,
Based on the planned inputs and outputs, the stages required for the design, duration, resources, required competencies, legal and other requirements to be complied with, control and validation activities can be determined and a design plan can be created with a meaningful whole consisting of all this data.
The design plan should be retained as documented information.
The prepared design plan will provide data for us to compare the planned and implemented design in the following stages.
During the design realization phase,
The data used in the design plan is used as input,
Planned reviews are implemented during the design period, and as a result of the reviews, either the design phase is approved and continued, or if there is a phase that is not approved, the necessary corrective action is implemented.
After the planned validation activity is successfully completed, the design and development outputs are collected. For example, after the validation activity phase of a machine whose prototype has been produced and works successfully is successfully completed, the design outputs are presented with the project completion report prepared.
8.4 Control of Externally Procured Processes, Products and Services
By preparing the purchasing process, conditions for the product and the supplier can be determined.
When determining supplier conditions, the nature and importance of the product purchased should also be taken into consideration.
For example;
If we consider that you are a company operating in the construction sector, concrete is a material with a high level of importance as it affects many factors such as the strength of the structure, safety, project duration, project budget, project reputation, a detailed supplier evaluation should be made before procuring.
For the concrete supplier;
Having the capacity to produce concrete in accordance with the desired qualities
Submission of material reports
Compliance with on-time delivery criteria (proximity and time to reach the construction site)
Achieving the expected criteria in the samples taken
Compliance with the company's payment terms (payment in TL, long-term payment, etc.)
Having ISO 9001, ISO 27001 certificates
Detailed criteria can be searched in the form.
If a supplier is considered from which stationery supplies are purchased for the same company, purchases made from this supplier will not directly affect the project and will not have high economic impacts. For this reason, for a supplier of this size, your company can determine the supplier criteria as a company that will comply with the company's management system by delivering the desired products on time in accordance with the planned budget.
Note: If you purchase a chemical substance, it is important to request the material safety report, known as MSDS, for safety purposes.
In order to record suppliers that meet the criteria in the purchasing process, an approved supplier list can be prepared and only work with approved suppliers can be done.
In addition, the performance of existing suppliers may be evaluated after the supply and, based on the evaluation results, a decision may be made whether the supplier in question will remain on the approved supplier list or be deleted.
8.5 Presentation of Products and Services
Determine the characteristics of the product and service produced and the results planned to be achieved and maintain relevant documented information.
Determine identification and traceability method and maintain relevant documented information.
Identify and secure external supplier ownership.
Secure the product or service output to maintain the desired conditions.
Define post-delivery activities
Review changes and record review results as documented information.
Note that the decision to change must be made by competent persons.
8.6. Launching of Products and Services
This article deals with the process of marketing and presenting the product or service to customers. The presentation of the product or service to the market is carried out in accordance with the planned marketing strategies and activities. This process includes steps such as the promotion, distribution, sale and delivery of the product or service. In addition, meeting customer demands and ensuring customer satisfaction is an important part of this process. Organizations take into account customer feedback regarding the presentation of the product or service to the market and, when necessary, work to improve their products or services. In this way, products or services that meet customer expectations and provide competitive advantage are presented.
9. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation
In your company, you should evaluate the information security performance and the effectiveness of the information security management system and determine the following.
a) What needs to be monitored and measured, including information security processes and controls,
b) Appropriate monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation methods to ensure valid results.
c) When monitoring and measurement will be done,
d) Who will do the monitoring and measuring?
e) When will monitoring and measurement results be analyzed and evaluated?
f) Who will analyze and evaluate these results.

Effectiveness of ISMS Processes performance
• Management review results
• Internal audit practices
• Improvement studies
• Corrective action practices
• ISMS awareness
• ISMS Trainings
• Security incident management, cost, lessons learned
• Password quality, patch management, access rights
• Reactions to attacks
• Physical access controls
•Etc.
9.2 Internal Audit
In your company, the information security management system
a) Complies with ISO 27001 and the company's ISMS standards.
b) It is effectively implemented and sustained,
To control, internal audits should be carried out at planned intervals.
The following factors are necessary regarding internal auditing in your company;
c) Planning, creating, implementing and maintaining the internal audit program, which also describes the frequency, methods and responsibilities. (Critical processes should be prioritized in the program)
d) Definition of audit criteria and scope for each audit,
e) Selection of auditors and conduct of audits in a way that ensures impartiality and objectivity,
f) Ensuring that audit results are reported to the appropriate management level.
g) Preservation of written evidence of the audit program(s) and audit results.

9.3 Management Review
Top management should review the ISMS at planned intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, accuracy and effectiveness.
The management review should address the following:
a) Status of the tasks from previous YGGs,
b) Changes in external and internal issues concerning ISMS,
c) Feedback on ISMS performance, including developments in:
1) Nonconformities and corrective actions,
2) Monitoring and measurement results,
3) Inspection results and
4) Fulfillment of information security objectives
d) Feedback from relevant parties,
Risk assessment results and status of risk treatment plan
Opportunities for continuous improvement.

The management review outputs should include decisions on opportunities for continuous improvement and any needs for changes required in the information security management system.
10. IMPROVEMENT
10.1 Non-Conformity and Corrective Action
In case of detection of non-conformity;
Check and fix if possible
To prevent the nonconformity from recurring or occurring elsewhere.
Look over
Determine root cause
Determine the occurrence or likelihood of occurrence of similar nonconformity
3. Implement corrective action
4. Review the effectiveness of corrective actions
5. If necessary, make improvements to the non-conformity in the ISMS.
Your company must retain written information as evidence of:
Reason for nonconformities and corrective actions implemented
Results of corrective action taken.
10.2 CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
The organization must continuously improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of its information security management system.
The organization should consider the results of the analysis and assessment and the outputs of the management review to determine whether there are needs or opportunities to be addressed as part of continual improvement.
Nonconformities should be monitored and corrective actions should be planned, risks should be identified and activities should be planned to eliminate/reduce them, opportunities should be identified and activities should be planned to improve them.
Process performances should be continuously monitored and performance evaluations should be made to check whether the desired performances are achieved in the processes. If the desired performance is not determined from the processes, remedial activities should be planned for the processes.
APPENDIX A
A.6 INFORMATION SECURITY ORGANIZATION

MOBILE DEVICES AND REMOTE WORKING
Use of devices such as phones, tablets, computers, etc.;
The use of mobile devices containing company data by employees should be controlled, risks should be identified, and an action plan should be implemented to reduce or eliminate risks. Mobile device use should be secured by policy.
The policy should also cover the following items:
a)Registration of mobile devices
b) Physical protection requirements
c) Software installation restrictions
d) Requirements for mobile device software versions and application of patches,
e) Restriction of connection to information services,
f) Access controls,
g) Cryptographic techniques,
h) Malware protection,
i) Remote disabling, deleting or locking,
j) Backup,
k) Use of web services and web applications.
Working remotely;
If the personnel work remotely for a permanent or certain period of time, information security risks that may arise such as connecting to the company system from a foreign network, losing company information, having it stolen, compromising the integrity of the information, etc. should be investigated and precautions should be taken against these risks. After the necessary opportunities are provided to the personnel, a policy should be prepared and remote working should be secured.
Main risks;
• Leaving the device on in the working environment
• Passwordless device usage
• Sharing passwords or devices with strangers
• Write the password on a notepad and leave it lying around.
• Commonly used passwords
• Repetitive password use
• Insufficiently secure passwords (Gozde.123456yedi)
A.7 HUMAN RESOURCES SECURITY

AWARENESS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ISMS
Management should encourage employees and contractors to implement the company's ISMS requirements.
In order to ensure awareness of ISMS within the company and to implement it effectively, the training and documentation required by the staff should be provided, and a disciplinary process should be published for the staff to prevent any breach of information security.
LEAVING A JOB AND CHANGE OF DUTY
In case of employee or contractor leaving the job or change of duty, the information security responsibilities of the employee must be determined and notified to the employee.
A.8 ASSET MANAGEMENT



MEDIA PROCESSING
To prevent unauthorized disclosure, alteration, and destruction of information; • Portable media management should be according to the classification scheme determined by the company • Information that is not needed should be securely destroyed in accordance with official procedures. • Physical media transmission containing information must be protected against unauthorized access, misuse and corruption. |
A.9 ACCESS CONTROL
• Create and publish a written access control policy
• Assign personal confidential identification information and provide information about usage rules
( Password management systems must be interactive and have adequate security levels. )
• Allow personnel to access only the network and files they are authorized to
• Determine methods for controlling and restricting privileged access rights
• Check users' access rights at regular intervals
• Cut off access to all information for personnel or related parties whose ties with the company have been terminated.
To manage access rights, process(es) that support the above items, cover all users and information, and manage user registration/deletion and secure login issues should be prepared and implemented.
Additionally, access to program source code should be restricted and the use of applications that can override system and application controls should be restricted and tightly controlled.
A.10 CRYPTOGRAPHY
CRYPTOGRAPHY
It is also shown as all the techniques used to convert readable information into an unreadable form by unwanted parties.
Caesar Cipher Method
Example: info =elojl
CRYPTOGRAPHIC CONTROLS
• A policy on the use of cryptographic controls to protect information should be prepared and implemented.
• A policy explaining the use, protection and lifetime of cryptographic keys should be prepared to ensure compliance with the policy.
A.11 PHYSICALLY AND ENVIRONMENTALLY SAFE
SAFE AREAS To protect sensitive and critical information resources; • Safe area boundaries must be determined and protected. • Only authorized personnel should be granted access and necessary access controls should be carried out. • Offices and facilities should be designed in accordance with physical security rules. • Information resources should be protected against negative external effects such as natural disasters, accidents, and malicious attacks. • Access points such as delivery and loading areas where unauthorized persons can enter the facility should be controlled and, if possible, separated from information processing facilities to prevent unauthorized access. |
Procedures for working in safe areas should be designed and implemented.
EQUIPMENT
• Must be protected against risks arising from environmental threats and unauthorized access.
• It should be protected against errors that may cause interruptions such as power outages etc.
• Power and telecommunication cables must be protected against eavesdropping, interference or damage.
• System continuity should be ensured by performing necessary maintenance.
• Information or software should never be taken outside the company without authorization.
• For assets outside the company, external risks related to the region should be determined and necessary precautions should be taken.
• Before destroying or reusing equipment containing storage media, it must be ensured that all sensitive data and licensed software are removed or securely overwritten.
• In environments where there is no surveillance, users must be assured of using the equipment appropriately. (Responsibilities can be announced through a policy or users can be guaranteed by signing)
• Clean desk and clean screen practices should be adopted.
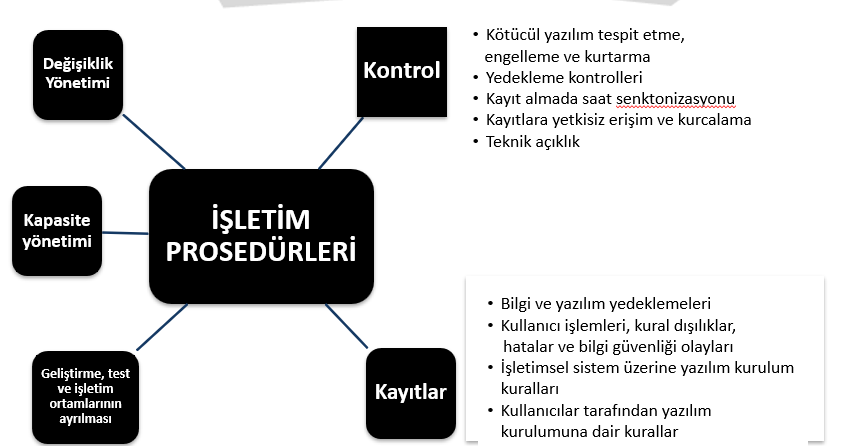
A.12 OPERATIONAL SECURITY
A.13 COMMUNICATIONS SECURITY
NETWORK SECURITY MANAGEMENT
Networks must be managed and controlled to protect information in systems and applications.
The security requirements of all network services should be determined and included in network services agreements.
Information services, users and information systems groups should be separated.
INFORMATION TRANSFER
• Controls must be carried out in accordance with transfer policies and procedures for information transfer.
• Information shared with external parties must be secured by preparing the necessary agreements.
• Information shared via e-mail must be protected in accordance with policy.
• Needs to be determined against privacy violations and secured with a confidentiality agreement. The agreement should be reviewed regularly .

A.14 SYSTEM PROCUREMENT DEVELOPMENT AND MAINTENANCE
SECURITY REQUIREMENTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Requirements regarding information security should be determined and included in the ISMS.
Information in application services passing over public networks must be protected from fraudulent activity, contractual disputes, and unauthorized disclosure and alteration.
Information in application service operations must be protected to prevent incomplete transmission, misdirection, unauthorized message modification, unauthorized disclosure, unauthorized message duplication, or message re-creation.
PROTECTION OF TEST DATA
Test data must be carefully selected, protected and controlled.
SECURITY IN DEVELOPMENT AND SUPPORT SYSTEMS
• Software and systems development rules must be determined and implemented.
• System changes should be controlled through the use of formal change control procedures.
• When operating platforms are changed, critical applications should be reviewed and tested to prevent adverse impact to corporate operations or security.
• Changes to software packages should be restricted and controlled to only necessary changes.
• System engineering principles should be determined, put into writing and applied to all information system studies.
• Secure development environments must be established and maintained for system development.
• Supervise and monitor externally provided system development activity
• Testing of security functionality should be performed during development.
• Acceptance test programs and related criteria should be determined for new information systems, upgrades and new versions.
A.15 SUPPLIER RELATIONS
INFORMATION SECURITY IN SUPPLIER RELATIONS ❑ A policy should be prepared and implemented to manage supplier relationships. ❑ Information security requirements should be agreed upon with suppliers who have access to the information or who provide the infrastructure for the information. ❑ Monitor, review and audit suppliers' services at regular intervals. ❑ Changes in supplier services should be reflected in the ISMS by evaluating their risks and impact on processes. |
A.16 INFORMATION SECURITY VIOLATION INCIDENT METHOD
• Responsibilities should be determined and procedures should be prepared to respond to violations quickly, effectively and regularly.
• Violations should be reported as quickly as possible.
• All users should be required to report any suspicious events they encounter in systems or services.
• Information security incidents should be evaluated and a decision should be made as to whether they will be classified as information security breaches.
• Violations must be responded to in accordance with procedures.
• Experience gained from analyzing and resolving information security breach incidents should be used to prevent potential breach incidents.
• Define and implement procedures for the description and management of information to collect evidence.
A.17 INFORMATION SECURITY ISSUES OF BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT
A.18 COMPLIANCE
The laws and contractual issues that must be implemented regarding the ISMS must be put in writing and kept up to date by constantly monitoring.
Appropriate procedures should be prepared to ensure compliance with legal requirements and contractual terms regarding intellectual property rights and the use of patented software.
Records must be protected against loss, destruction, forgery, unauthorized access and unauthorized publication in accordance with all requirements affecting the ISMS.
In case of the existence of personal identification information, necessary measures should be taken for the confidentiality and protection of the information, taking into account the relevant laws and rules.
Cryptographic controls must be used in compliance with all relevant contracts, laws and regulations.
































Comments