ISO - 45001
- gözde alnıaçık
- Jun 1, 2024
- 1 min read
4. CONTEXT OF THE ORGANIZATION
Identifying the factors affecting your company will guide you in setting up your system.
4.1 Understanding the Context of the Organization
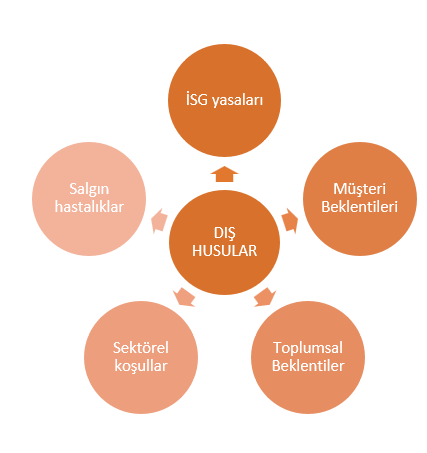
In this step, the sector in which the organization operates, the business environment, legal requirements and other external factors are examined. Factors such as the organization's founding purpose, date, size and geographical location are also taken into consideration. For this purpose, interviews can be conducted with managers, employees and external stakeholders, and industry analyzes and market research can be conducted.
For example, for a construction company, the context of the organization may include factors such as the general economic situation of the industry, competitive structure, legal regulations, occupational safety standards and project diversity.
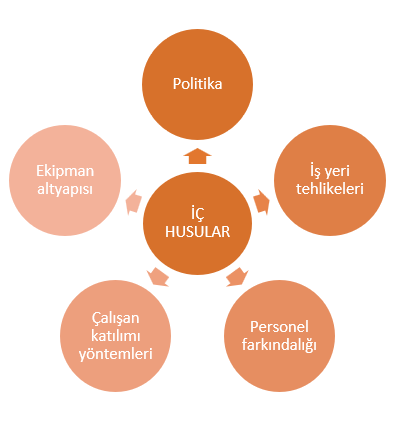
Note: Internal and external issues are randomly sampled with a general approach, you need to customize and detail specific to the scope of your company.
4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Employees and Other Interested Parties
Relevant parties that affect the operation of the company should be identified and the environmental needs and expectations of these parties should be determined. In ISO 45001, it is necessary to focus on reaching and understanding the needs and expectations of employees.
The internal and external issues specified in Article 4.1 are guiding in the determination of the relevant parties.
For example, for a hotel business, relevant parties may include the occupational safety and health expectations of employees, the comfort and security expectations of customers, and the demands of local communities to reduce environmental impacts.
4.3 Scope
The scope of the organization's Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) management system is determined. This involves defining which business units, processes or activities fall within the scope of the OH&S management system.
When determining the scope, the sector in which the organization operates, risk profile, legal regulations and stakeholder expectations should be taken into consideration.
For example, the OH&S management system scope for a factory may include specific business areas such as production line operations, warehouse activities, and office functions.
4.4 Management System and Processes
The administrative, support and operational processes necessary to improve your company's OHS performance should be determined and defined in accordance with the ISO 14001 standard . These processes may include the establishment of OSH policies, risk assessment and control, training and awareness programs, emergency planning and monitoring and measurement activities.
Processes should be constantly reviewed and updated when necessary, based on continuous improvement principles.
5. LEADERSHIP
5.1 Leadership and Commitment
Top management must show leadership for the occupational health and safety management system to function effectively. In this context,
An occupational health and safety policy should be established and processes in accordance with this policy should be determined.
Senior management should encourage continuous improvement of occupational health and safety performance by adopting a risk and opportunity-based approach.
5.2 OHS Policy
A formal OSH policy should be established that includes the organisation's OSH objectives and commitments. This policy is a fundamental document that guides and supports the organization's OHS performance.
5.3 Duties, Powers and Responsibilities
Top management must determine the duties, authorities and responsibilities for the effective functioning of the occupational health and safety management system. In this context,
The roles, authorities and responsibilities established for OSH management should be clarified. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of OHS managers, OSH representatives and other employees.
Deputizing positions for critical positions should be determined and business continuity should be ensured.
5.4 Obtaining Employee Opinions and Employee Participation
Employees' opinions and feedback on OHS issues are important. The organization should establish mechanisms to encourage employee participation and actively engage employees in safety and health issues.
6. PLANNING
6.1 Risk and Opportunity Identification Activities
Your company should make plans to identify OHS risks and identify opportunities. This includes overall risk assessment, hazard identification, determination of legal requirements and planning activities.
6.2 OSH Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them
Necessary activities are planned to achieve the company's determined OHS Targets. This planning process includes the strategies, programs and projects to be followed to achieve OHS objectives. In addition, the resources, duration and responsibilities of these activities are also planned. These activities are effectively implemented and monitored to continuously improve OHS performance.
7. SUPPORT
7.1 Resources
It must provide the necessary resources for the OHS management system. This includes human resources, financial resources, infrastructure and other requirements.
7.2 Competence
Your company must determine the competencies of the personnel working within the OHS Management System and ensure these competencies.
In addition, if necessary, the company should plan the necessary training to provide its personnel with new competencies.
The competencies required for each personnel included in the OHS management system should be determined, and personnel with these competencies should be preferred when recruiting personnel.
In case the specified competencies are missing or new competencies are needed, the necessary training opportunities must be provided to the personnel to provide them with new competencies.
7.3 Awareness
It must ensure that all personnel working within the OHS Management system are aware of the following:
a) OHS policy,
b) OHS objectives
c) Contributions to OHSMS effectiveness,
d) Effects that will occur as a result of not fulfilling OHSMS requirements
Orientation training can be given to newly hired personnel about the company's general management systems and the processes they will work in, and management systems awareness training can be given to all personnel regularly every year. Records of the training provided should be kept.
7.4 Communication
It is necessary to give clear answers to the following items by determining the internal and external communication methods in your company. This includes information sharing among staff, communication with customers, suppliers and other interested parties.
The company's communication methods and communication tools should be determined and announced to the relevant personnel.
Accessibility of communication resources such as phone numbers and e-mail addresses should be ensured.
7.4.1 General
The general communication strategy and procedures regarding the organization's environmental management system are determined.
7.4.2 Internal Communication
Communication processes and channels within the organization ensure that information regarding the OSH management system is effectively communicated among personnel.
7.4.3 External Communication
Communication processes and channels with stakeholders outside the organization ensure that information about the OSH management system is effectively communicated with customers, suppliers, the public and other stakeholders.
7.5 Documented Information
Defines, creates, updates and maintains documented information regarding the OHS management system. This information may include procedures, instructions, policies, records and other documents.
An in-house document format can be prepared (using logo, letterhead, standard writing format and standard templates).
In addition, for each document, a document number and document name should be given according to the management determined within the company.
Prepared documents should be used after being reviewed and implemented by a competent personnel,
In addition, all documents must contain preparer and approver information.
In addition to preparing the documents, accessibility of the documents to the relevant persons and confidentiality of the necessary documents must be ensured.
8. OPERATION
8.1 Operational planning and control
It carries out operational planning and control activities to achieve the targets determined within the scope of the OHS management system. These activities aim to improve OHS performance such as preventing hazards, reducing/preventing risks, developing opportunities and meeting employee expectations. The operational planning and control process includes steps such as allocating the resources necessary to achieve the determined goals, determining and monitoring operational processes and taking necessary corrective measures.
8.2 Emergency preparedness and response
It is necessary to be prepared for OHS-related emergencies and take the necessary precautions to deal with these situations effectively. Emergency preparedness activities include assessing OHS risks and hazards, developing emergency plans, training personnel and organizing emergency drills. The aim of this process is to prevent work accidents, protect personnel health and minimize hazards.
9. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation
OHS performance should be monitored, measured, analyzed and evaluated regularly. This includes activities such as compliance assessments, internal audits and management reviews.
9.2 Internal Audit
By preparing the internal audit process, the internal audit and its conditions can be described.
While preparing the process, care should be taken to ensure that the internal audit is carried out by competent persons at least once a year.
The following factors are necessary regarding internal audit in your company
Planning, creating, implementing and maintaining the internal audit program, which also describes frequency, methods and responsibilities. (Critical processes should be given priority in the program)
Defining the audit criteria and scope for each audit,
Selection of auditors and conduct of audits to ensure impartiality and objectivity,
Ensuring that audit results are reported to the appropriate management level
Preserving written information that constitutes evidence of the audit program(s) and audit results.
9.3 Management Review
Top management periodically reviews the effectiveness and suitability of the environmental management system. These review meetings include evaluating environmental performance, reviewing policies and objectives, evaluating internal and external factors, and identifying improvement opportunities.
10. IMPROVEMENT
10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action
OSH incidents and nonconformities should be reported, investigated and corrective actions implemented. For the detected non-conformity, a non-conformity report should be prepared and the root cause should be determined first, the root cause should be identified and corrective action should be planned to prevent the recurrence of the non-conformity. If non-conformance occurs in other departments or other areas, the non-conformity report is closed after checking if it occurs, making all necessary corrections and taking actions to prevent recurrence. The closed report must be approved by an authorized personnel.
10.2 CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
The organization must continuously improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of its OSH management system.
The organization should consider the results of the analysis and evaluation and the outputs of the management review to determine whether needs or opportunities exist to be addressed as part of continuous improvement.
Nonconformities should be monitored and corrective actions should be planned, risks should be identified and activities aimed at eliminating/reducing them should be identified and opportunities for improvement should be planned.
Process performances should be constantly monitored and performance evaluated to check whether the desired performances are achieved in the processes. If the desired performance is not detected from the processes, remedial action must be planned for the processes.




Comments