ISO - 9001
- gözde alnıaçık
- Jun 1, 2024
- 0 min read
4. CONTEXT OF THE ORGANIZATION
Identifying the factors affecting your company will guide you in setting up your system.
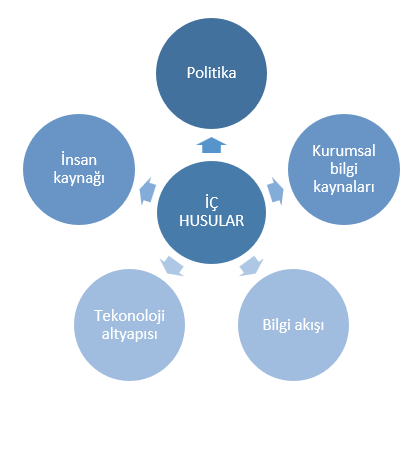
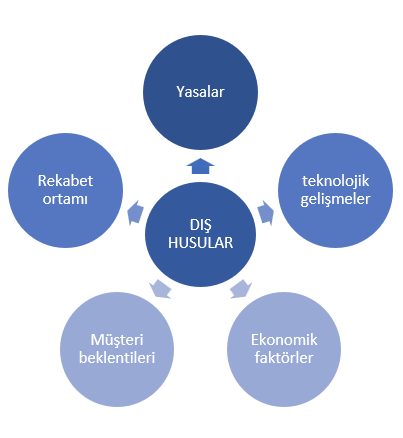
4.1 Understanding the Context of the Organization
The factors that the management system affects and is affected by should be determined as context.
The issues that are affected can be defined as the external context, and the issues that it affects can be defined as the internal context.
Note: Internal and external issues are randomly sampled with a general approach, you need to customize and detail specific to the scope of your company.
4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Relevant Parties
Relevant parties that affect the operation of the company should be identified and the environmental needs and expectations of these parties should be determined.
The internal and external issues specified in Article 4.1 are guiding in the determination of the relevant parties.
For example;
When we take as an example a company that produces and sells shoes,
In this company, human resources are determined as an internal issue and legal requirements are determined as an external issue.
When we examine the internal issue of human resources, this brings us to the relevant parties such as management, blue collar personnel, white collar personnel,
When we examine the external legal conditions, we see that we are affiliated with the relevant party of the Ministry of Commerce since we are a trading company.
We need to examine the relevant parties we have identified and question their needs and expectations.
The following results will be obtained as a result of the query.
Needs and expectations of blue-collar personnel: On-time payment, safe working environment, social rights, etc.
Ministry of Commerce needs and expectations: Compliance with relevant laws
4.3 Scope
In the scope, you should describe the work areas and areas of activity that determine the boundaries of your company.
Additionally, if there is a substance that you exclude from the standard, you must describe it here with justification.
For example,
If we examine the scope of the company SÜT.AŞ, which produces and sells milk.
SÜT.AŞ carries out its production activities in its 1000 m2 production facility at Tokat Niksar ..... and carries out its sales activities in its 300 m2 sales office located at ..... in Tokat Center.
Since there is no design activity in our company, the ISO 9001 / ''8.3 Design and Development of Products and Services'' clause is excluded in our system.
4.4 Management System and Processes
The administrative, support and operational processes your company needs should be determined and the procedures should be described in accordance with ISO 9001 with the determined method. These processes may be aimed at measuring/improving customer satisfaction, evaluating process performance, organizing training, implementing internal audits, and organizing corrective actions. In addition, apart from these examples, necessary planning, application control, etc. in accordance with the company's own operations. Operational processes should also be prepared for the stages.
You can describe your process under a procedure, draw a flow chart, or determine an alternative method.
Processes should be constantly reviewed and updated when necessary, based on continuous improvement principles.
Below, an example of a process interaction diagram prepared for a company engaged in Engineering Management and R&D activities is given, and immediately afterwards, an example of the "Internal Audit Process" prepared with the logic of a process flow chart according to the process requirements of the internal audit process in the diagram is shared.
Note: The examples shared in the figures above are entirely based on assumption. They can be changed or developed according to the scope, areas of activity and company structures of the companies.
5. LEADERSHIP
5.1 Leadership and Commitment
5.1.1 General
5.1.1 General
by top management,
A quality policy in line with company strategies should be established, processes consistent with the policy should be prepared and quality targets should be determined.
While displaying this leadership approach, senior management should exhibit a risk and opportunity-based approach and encourage continuous improvement by providing the necessary resources.
5.1.2 Leadership and Commitment
By preparing a process that records customer wishes and complaints, efforts can be made to realize wishes and prevent complaints.
By preparing a customer satisfaction evaluation process, customer satisfaction can be questioned through satisfaction surveys.
In the factors where dissatisfaction is detected at the end of the process, the cause of dissatisfaction should be investigated and action for improvement should be planned.
5.2 Policy
A quality policy should be established by top management that is appropriate to the company's purpose and context, provides strategic direction, meets applicable requirements and provides a framework that includes a commitment to continuous improvement of the quality management system.
Policy;
It must be specific and appropriate to your company
Must be announced to all company employees and other relevant parties
For the announcement process,
The Approved Policy can be shared with staff and visitors by hanging it on the announcement board or at visible points in the company.
It can be shared on the website and made accessible to all interested parties.
It can be shared with staff in a common system that all staff can access,
Or, apart from these, the company may apply its own alternative Policy announcement method.
5.3 Duties, Powers and Responsibilities
In order to ensure the continuity of the quality management system and to operate the processes, duties, authorities and responsibilities must be determined, announced and secured.
An organizational chart should be prepared and then the duties, authorities and responsibilities for each position in the chart should be defined.
While determining duties, authorities and responsibilities, it is recommended to determine positions that will act as substitutes in case of vacancy for critical positions, in order to ensure business continuity in case of unplanned long-term vacancy of any position, such as resignation, illness, change of duty.
6. PLANNING
6.1 Risk and Opportunity Identification Activities
Processes should be evaluated on a risk and opportunity basis, and an action plan should be made to prevent/mitigate risks and improve opportunities.
Risks and opportunities and developing action plans should be announced to process owners and, if deemed necessary, necessary revisions should be made in the processes.
Risks and opportunities should be constantly monitored and it should be evaluated whether the planned actions are functional or not, and if the action plan does not create the desired effect, a new action plan should be made .
6.2 Goals and Planning to Achieve Them
Necessary activities are planned to achieve the company's determined Quality Targets. This planning process includes the strategies, programs, and projects to be followed to achieve quality objectives. In this context, organizations should adopt a smart (specific, measurable, accessible, relevant and time-bound) approach when setting quality goals and plan resources and processes to achieve these goals. In addition, the resources, duration and responsibilities of these activities are also planned. These activities are effectively implemented and monitored to continuously improve quality performance.
6.3 Planning Changes
In case of a change that will affect the quality management system
a) Purposes and potential consequences of the changes
b) Effect of the integrity of the quality management system
c) Availability of resources required for change
d) Authorities and responsibilities regarding change
You should make an analysis about it and decide on changes as a result of this analysis.
Before any change decision that will affect the management system is taken,
-What will be done, when, how, by whom and with what resources should be determined.
-Are the resources available for change sufficient? New resource needs, if any, should be determined.
- The impact of the change on the company should be investigated.
And the change should be made after the change report prepared after the requested analyzes are completed and approved by a personnel authorized for the change.
7. SUPPORT
7.1 Resources
7.1.1
The resources needed to fulfill the quality management system requirements are determined, provided and maintained. These resources may include human resources, infrastructure, work environment and financial resources.
Note: The examples shared above are entirely based on assumption. They can be changed or developed according to the scope, areas of activity and company structures of the companies.
7.1.2 Contacts
Your company must determine how it will select new human resources and how its existing human resources will be adapted to the company's quality management systems.
For this purpose, a human resources process can be prepared and a method can be described for personnel selection in accordance with the quality management system and in line with the company's expectations.
After selecting personnel that meet the company's expectations, the newly hired personnel should be given the necessary administrative and technical orientation so that they can learn and adapt to the company's quality management systems and the process in which they will work.
In addition, in order to ensure the awareness of the existing human resources about the company's quality management system and to ensure continuity in system adaptation by being informed of changes in the standard or the company's quality management system, if any, regular training should be given to all personnel explaining the relevant standards and the company management system.
Note: Records of the orientation training given to on-the-job personnel and the awareness training provided regularly to all personnel should be kept as documented information.
7.1.3 Infrastructure
All buildings, facilities, machinery equipment, software, hardware, transportation resources, information and communication technology, etc. that constitute the infrastructure of the organization. A list of infrastructure resources such as these should be made and a tracking method should be determined for each.
In addition, the control interval should be determined for each infrastructure resource according to its own needs and the control results should be processed when the time comes.
7.1.4 Environment for operation of processes
By describing the social, psychological and social environment needed for the processes within all processes, the existence or availability of the desired environment can be interpreted at the process control stage.
7.1.5 Monitoring and measurement resources
7.1.5.1 General
You can keep track of what will be subject to monitoring and measurement in your company by creating a monitoring and measurement tracking list.
For example: Your list: Customer satisfaction
Process performance effectiveness
Internal audit results
Degree of achieving goals
Amount of energy use (electricity, water, natural gas, oil)
Assuming that it consists of contents, a separate monitoring and measurement criterion should be determined for each item here, and the control results should be processed and evaluated by checking them at intervals determined by the system.
7.1.5.2 Measurement Traceability
The validity of the measurement must be proven by calibrating the equipment used for measurement at regular intervals in accordance with international standards.
For this purpose, a calibration tracking list can be prepared and the devices subject to calibration and calibration criteria can be entered into the list and calibration tracking can be done through this list.
7.1.6 Corporate Information
7.2 Competence / Qualification
Your company must determine the competencies of the personnel working within the Quality Management System and ensure these competencies.
In addition, if necessary, the company should plan the necessary training to provide its personnel with new competencies.
The competencies required for each personnel in the organizational chart should be determined, and personnel with these competencies should be preferred when recruiting personnel.
In case the specified competencies are missing or new competencies are needed, the necessary training opportunities must be provided to the personnel to provide them with new competencies.
7.3 Awareness
The management must ensure that all personnel working within the system are aware of the following:
a) Quality policy,
b) Quality objectives
c) Contributions to the QMS effectiveness,
d) The effects that will occur as a result of not fulfilling the QMS requirements
Orientation training can be given to newly hired personnel about the company's general management systems and the processes they will work in, and management systems awareness training can be given to all personnel regularly every year. Records of the training provided should be kept.
7.4 Communication
It is necessary to give clear answers to the following items by determining the internal and external communication methods in your company. This includes information sharing among staff, communication with customers, suppliers and other interested parties.
The company's communication methods and communication tools should be determined and announced to the relevant personnel.
Accessibility of communication resources such as phone numbers and e-mail addresses should be ensured.
7.5 Documented Information
Defines, creates, updates and maintains documented information regarding the quality management system. This information may include procedures, instructions, policies, records and other documents.
An in-house document format can be prepared (using logo, letterhead, standard writing format and standard templates).
In addition, for each document, a document number and document name should be given according to the management determined within the company.
Prepared documents should be used after being reviewed and implemented by a competent personnel,
In addition, all documents must contain preparer and approver information.
In addition to preparing the documents, accessibility of the documents to the relevant persons and confidentiality of the necessary documents must be ensured.
8. OPERATION
8.1 Operational Planning and Control
It is necessary to prepare process(es) for the product or service.
The process can be described in a procedure or methods such as flow charts and process cards can be used.
The important thing here is that the prepared processes comply with the process preparation criteria given in the article '4.4 Quality management system and processes'. Generally speaking, the necessary conditions and resources for the processes should be determined, the necessary control method should be planned and implemented.
Identify, maintain and maintain documented information to the extent necessary to ensure:
1) To ensure that processes are operated as planned,
2) To demonstrate compliance with the conditions of products and services.
The outcome of planning should be appropriate to the organization's operations.
The organization must control planned changes and review the consequences of undesirable changes by carrying out the necessary actions to reduce their negative effects.
The organization must ensure that the processes it outsources are controlled (see Clause 8.4).
8.2 Terms for Products and Services
This article deals with the conditions that organizations set for the products they produce or the services they provide. The requirements of the product or service and customer expectations form the basis of the specified terms. During the planning process, the necessary features, attributes, performance criteria and other requirements of the product or service are determined. These are important elements that determine the quality level of the product or service. Additionally, the specified requirements provide guidance during the design and production stages of the product or service. In this context, customer requirements, legal regulations, standards and the organization's own policies and procedures are taken into account when determining the terms of the product or service.
8.3 Product and Design Development
Planning for the design must be done before the design takes place.
A planning process was prepared for this and
Based on the planned inputs and outputs, the necessary stages for the design, duration, resources, required competencies, legal and other requirements to comply with, control and validation activities can be determined and a design plan can be created with a meaningful whole consisting of all these data.
The design plan should be maintained as documented information.
The prepared design plan will provide data for comparing the planned and implemented design in the following stages.
During the design phase,
The data used in the design plan is used as input,
Planned reviews are implemented throughout the design period, and as a result of the reviews, the design phase is either approved and continued, or if there is a phase that is not approved, the necessary corrective action is taken.
Once the planned validation activity is successfully completed, the design and development outputs are collected. For example, after the validation activity phase of a machine whose prototype has been produced and works successfully is completed successfully, the design outputs are presented with the project completion report.
8.4 Control of Outsourced Processes, Products and Services
By preparing the purchasing process, conditions for the product and supplier can be determined.
The nature and importance of the product purchased should also be taken into consideration when determining the supplier's conditions.
For example;
Considering that you are a company operating in the construction industry, concrete is a material of high importance as it affects many factors such as the durability of the structure, safety, project duration, project budget, project reputation, and a detailed supplier evaluation should be made before supplying it.
For concrete supplier;
Having the capacity to produce concrete in accordance with the desired qualities
Presenting material reports
Compliance with on-time delivery criteria (proximity and time to reach the construction site)
Reaching the expected criteria in the samples taken
Compliance with company payment terms (payment in TL, long-term payment, etc.)
Having ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001 certificates
Detailed criteria can be searched as follows.
If a supplier from whom stationery materials are purchased for the same company is considered, purchases made from this supplier will not directly affect the project and will not have high economic impacts. For this reason, for a supplier of this caliber, your company will comply with the company's QMS by delivering the desired products on time in accordance with the supplier criteria and the planned budget. can be designated as a company that will provide
Note: If you purchase a chemical substance, it is important to request the material safety report, known as MSDS, for safety purposes.
In order to register suppliers that meet the criteria in the purchasing process, an approved supplier list can be prepared and only approved suppliers can be worked with.
In addition, the performances of the existing suppliers are evaluated after the supply and according to the evaluation results, it can be decided whether the supplier in question will remain on the approved supplier list or be deleted.
8.5 Delivery of Products and Services
Determine the characteristics of the product and service produced and the results planned to be achieved and maintain relevant documented information.
Maintain documented information on identification and traceability method
Identify and secure ownership of the external supplier.
Secure product or service output to maintain desired conditions.
Define post-delivery activities
Review changes and record review results as documented information.
Note that the decision to change must be made by competent people.
8.6 Launch of Products and Services
This article deals with the process of marketing the product or service and offering it to customers. The introduction of the product or service to the market is carried out in line with planned marketing strategies and activities. This process includes steps such as promotion, distribution, sale and delivery of the product or service. Additionally, meeting customer demands and ensuring customer satisfaction is an important part of this process. Organizations take into account customer feedback regarding the launch of the product or service and work to improve their products or services when necessary. In this way, products or services that meet customer expectations and provide competitive advantage are offered.
9. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation
This clause addresses the processes required to monitor, measure, analyze and evaluate the performance of the quality management system. Monitoring and measurement activities help the organization evaluate quality performance and direct continuous improvement efforts. These processes are used to evaluate the achievement of established quality objectives.
Monitoring and measurement activities are carried out using determined critical performance indicators (KPIs). These indicators aim to measure performance in various areas such as customer satisfaction, product quality, service performance, process efficiency. Monitoring and measurement results are regularly collected, analyzed and reported.
The analyzed data is used to evaluate the effectiveness of the quality management system. These analyzes are used to identify improvement opportunities in processes, identify potential problems in advance, and continuously improve quality performance.
Evaluation processes evaluate the suitability, effectiveness, and continuous improvement efforts of the organization's quality management system. This is accomplished through evaluation processes, internal audits, management review and other appropriate methods.
As a result, monitoring, measuring, analyzing and evaluating processes help organizations continuously improve their quality management systems and increase customer satisfaction. These processes allow organizations to monitor quality performance, achieve specific goals, and continuously improve.
9.2 Internal Audit
By preparing the internal audit process, the internal audit and its conditions can be described.
While preparing the process, care should be taken to ensure that the internal audit is carried out by competent persons at least once a year.
The following factors are necessary regarding internal audit in your company
Planning, creating, implementing and maintaining the internal audit program, which also describes frequency, methods and responsibilities. (Critical processes should be given priority in the program)
Defining the audit criteria and scope for each audit,
Selection of auditors and conduct of audits to ensure impartiality and objectivity,
Ensuring that audit results are reported to the appropriate management level
Preserving written information that constitutes evidence of the audit program(s) and audit results.
9.3 Management Review
9.3.1 General
A YGG meeting should be held at least once a year, aiming to achieve the desired outputs using the inputs given above. should be recorded
9.3.2 Management review inputs
The management review should be planned and carried out taking into account the following:
a) Status of activities for which decisions were made in previous management reviews, b) Changes in internal and external matters related to the quality management system, c) Information regarding the performance and effectiveness of the quality management system, including trends regarding:1) Customer satisfaction and feedback from interested parties notifications, 2) Degree of achieving quality targets, 3) Conformity of process performance and products and services, 4) Non-conformities and corrective actions, 5) Monitoring and measurement results, 6) Audit results, 7) Performance of external suppliers. d) Adequacy of resources, e ) Effectiveness of activities carried out to identify risks and opportunities (see Article 6.1), f) Opportunities for improvement.
9.3.3 Management review outputs
All these issues should be evaluated at the QMS evaluation meeting prepared before the YGG meeting, using the inputs given as YGG input in the standard.
As a result of the meeting,
a) Opportunities for improvement, b) Any need for changes regarding the quality management system, c) Resources needed.
The outputs should be accessed and recorded as documented information in the meeting report format.
10. IMPROVEMENT
10.1 Nonconformity and Corrective Action
For the detected non-conformity, a non-conformity report should be prepared and the root cause should be determined first, the root cause should be identified and corrective action should be planned to prevent the recurrence of the non-conformity. If non-conformance occurs in other departments or other areas, the non-conformity report is closed after checking if it occurs, making all necessary corrections and taking actions to prevent recurrence. The closed report must be approved by an authorized personnel.
10.2 CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
The organization must continuously improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of its quality management system.
The organization should consider the results of the analysis and evaluation and the outputs of the management review to determine whether needs or opportunities exist to be addressed as part of continuous improvement.
Nonconformities should be monitored and corrective actions should be planned, risks should be identified and activities aimed at eliminating/reducing them should be identified and opportunities for improvement should be planned.
Process performances should be constantly monitored and performance evaluated to check whether the desired performances are achieved in the processes. If the desired performance is not detected from the processes, remedial action should be planned for the processes.




















Comments